Explain the Differences Between the Somatosensory and Motor Humunculi
We then can divide these general maps of motor and sensory areas into regions with more specific. Scientists can map which parts of the brain control various parts of the body.

Difference Between Motor And Sensory Homunculus Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
The primary somatosensory area S1 is present in the postcentral gyrus and the paracentral gyrus.

. Both are involved in sending outputs to the muscles motor functions. The proportions of the homunculus are the same as the proportions of the physical body. Sensory neurons carry information from receptors to the brain Motor neurons carry signals from the brain to muscles Interneurons convey information between different types of neurons.
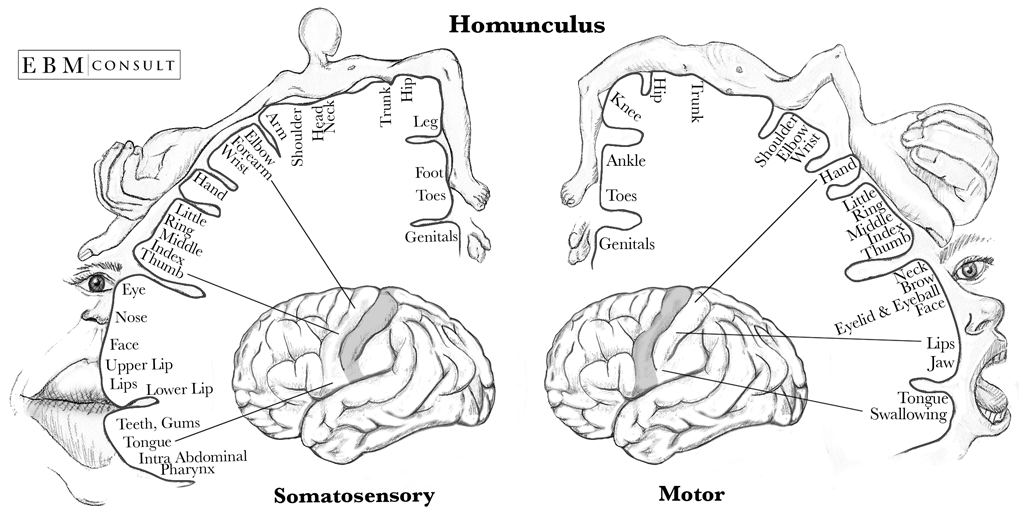
Motor homunculus present on the primary motor cortex of the precentral gyrus. IPSP or EPSP and action potential. Asked Aug 10 2019 in Psychology by Lisas physiological-and-bio-psychology.
Pain is a fact of life. In chronic pain there is a more widespread activation of the IC compared to acute pain. This homunculus represents how body parts feel whereas the motor homunculus represents how body parts move.
The IC is also more linked with sensory discrimination in chronic pain rather than emotional processing. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal. A cortical homunculus is a distorted representation of the human body based on a neurological map of the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor functions or sensory functions for different parts of the body.
The motor area located at the back of the frontal lobes of the brain controls voluntary movement. Sensory receptors housed in the dorsal root ganglia project to secondary neurons of the spinal cord that decussate and project to the thalamus or cerebellum. 13 of patients visiting the doctor complain.
Blankenburgs study pinpointed activity in a part of the brain called the somatosensory cortex an area that maintains an internal. Briefly describe the differences among sensory neurons motor neurons and interneurons 3 points each. We found some similarities to but also substantial differences from the seminal work of Penfield and colleagues.
Tertiary neurons project to the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe forming a sensory homunculus. At the most general level areas that control motor functions m uscle movement map to the front-most areas of the cerebral cortex while areas that receive and process sensory information are more towards the back of the brain Figure 1. The secondary somatosensory area S2 is present in the vicinity of the lateral fissure.
Cm2 with a thickness varying between 2-4 mm housing an estimated 10-30 billion neurons. Our focus will be on two specialized areas of the neocortex the primary motor and somatosensory cortex M1 S1 Figure 1a. Both areas are involved in receiving inputs from the senses sensory functions.
The ICs role in suffering is minimised so as to accommodate the vast increase in activation that is seen in S1 and S2. Explain to your roommate the significance of the somatosensory homunculus in terms of what it tells us about sensitivity to different parts of the body. The experiments explain how the circuitry of a region of the mouse brain called the somatosensory cortex which processes input from the various systems in the body that respond to the sense of touch can change.
The area of the homunculus that represents the foot is adjacent to the area for the hand. The motor homunculus is not to be confused with the sensory homunculus which is a sensory representation in the somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus. The somatosensory cortex is present in the parietal lobe.
We propose an updated version of the human motor homunculus and of its correlation with the somatosensory homunculus previously defined in MNI space with a similar brain mapping technique. 10 points for all three. What is Wilder Penfields primary somatosensory and motor cortices topographic organization homunculus.
The word homunculus is Latin for little man or miniature human and was a term used in alchemy and folklore long before scientific. The homunculus was developed by experimentally recording electrical potentials from cells in the somatosensory cortex during stimulation of various parts of the body. What are the three different structures of cytoskeleton and their functions.
The sensorimotor homunculus is also often depicted as a figure of a man with the size of parts of his body corresponding to the relative areas these parts have on the surface of the cortex. Average person will suffer 10 years of pain. What is the difference between graded potential eg.
Axons enter the spinal cord and synapse onto neurons on the contralateral side--ascend the spinal cord and join the medial lemniscus-- ventrolateral thalamus--- somatosensory cortex. The mapping is done by stimulating the sensory or motor cortex with a weak electric current. Somatosensory homunculus on the primary sensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.
The somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch as well as temperature body position and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system which also represents visual auditory olfactory and gustatory stimuli. Adjacent to this area of the brain is the sensory area in the parietal lobe.
About 90 of this sheet of neurons has six histologically defined layers and is called the neocortex. The somatosensory system consists of primary secondary and tertiary neurons. The primary somatosensory area S1 receives sensation from the contralateral half of the body.
Motor homunculus present in the internal capsule.

Comments
Post a Comment